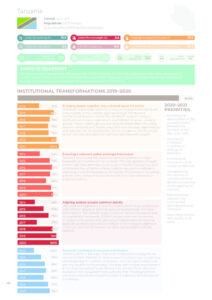
Nutrition situation
Under five stunting (%)
31.8
Under five overweight (%)
2.8
Anaemia in women 15-49 years (%)
37.2
Under five wasting (%)
3.5
Low birth weight (%)
10.5
0 to 5-month-old exclusive breastfeeding (%)
57.8
Adolescent overweight (%)
Male: 7
/ Female: 15.7
Adult overweight (%)
Male: 19.6
/ Female: 35.5
Adult obesity (%)
Male: 4
/ Female: 12.7
Adult diabetes (%)
Male: 6
/ Female: 6.1
COVID-19 snapshot
Tanzania has been less severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, and the Government has taken measures to contain spread of the virus. Out of the standard containment measures, public and private enterprises continue to operate. The authorities are assessing the economic impacts of COVID-19.
Institutional transformations 2019-2020
Bringing people together into a shared space for action
SUN multi-stakeholder platform actors are engaged and contribute meaningfully to the nutrition agenda through the National Multisectoral Nutrition Action Plan (NMNAP), midterm reviews, the Nutrition Compact agreement and NMNAP thematic working groups. These working groups including all stakeholders, including relevant ministries (incl. health, education and finance), departments and agencies, the United Nations, donors, academia and the private sector, who also provided both technical and financial support.Ensuring a coherent policy and legal framework
Tanzania has successfully sustained coherent policies and highlevel political commitment for nutrition. This was apparent through several high-level directives, such as use of fortified food products in schools and the utilisation of local tradition education methods in delivering nutrition messages to the public. The process of reviewing policies takes a long time and can hinder the implementation of proposed actions.Aligning actions around common results
The continual alignment of nutrition stakeholders’ plans and actions with NMNAP targets at national and subnational levels is a major achievement. The NMNAP and its Common Results, Resources and Accountability Framework (CRRAF) are key. Joint annual reviews of targets and capacity strengthening of stakeholders on national goals are good practices that contribute to an increased alignment of actions, also that of nutrition-sensitive sectoral plans with the NMNAP.Financial tracking and resource mobilisation
Tanzania plans to develop a resources mobilisation strategy for the second NMNAP (NMNAP II). Improvement has been seen in planning and budgeting for nutrition, at all levels, and financial tracking tools are very valuable to this process. One area with notable improvement is the disbursement of funds allocated for nutrition from domestic sources at the local government authority level. Tracking nutritionsensitive expenditures and prioritisation at subnational levels remain a challenge.2020-2021 Priorities
- Finalising the development of the second National Multisectoral Nutrition Action Plan 2021–2026.
- Developing a resource mobilisation strategy for NMNAP II.
- Finalising the creation of a SUN Academia Network.
- Strengthening the capacity of nutrition-sensitive sectors on planning and budgeting for nutrition.
- Mainstreaming nutrition into national and sectoral plans and strategies.
- Improving nutrition data quality, at all levels.
Download